Histopathology
The testing utilizes the latest technologies to provide the most accurate results.
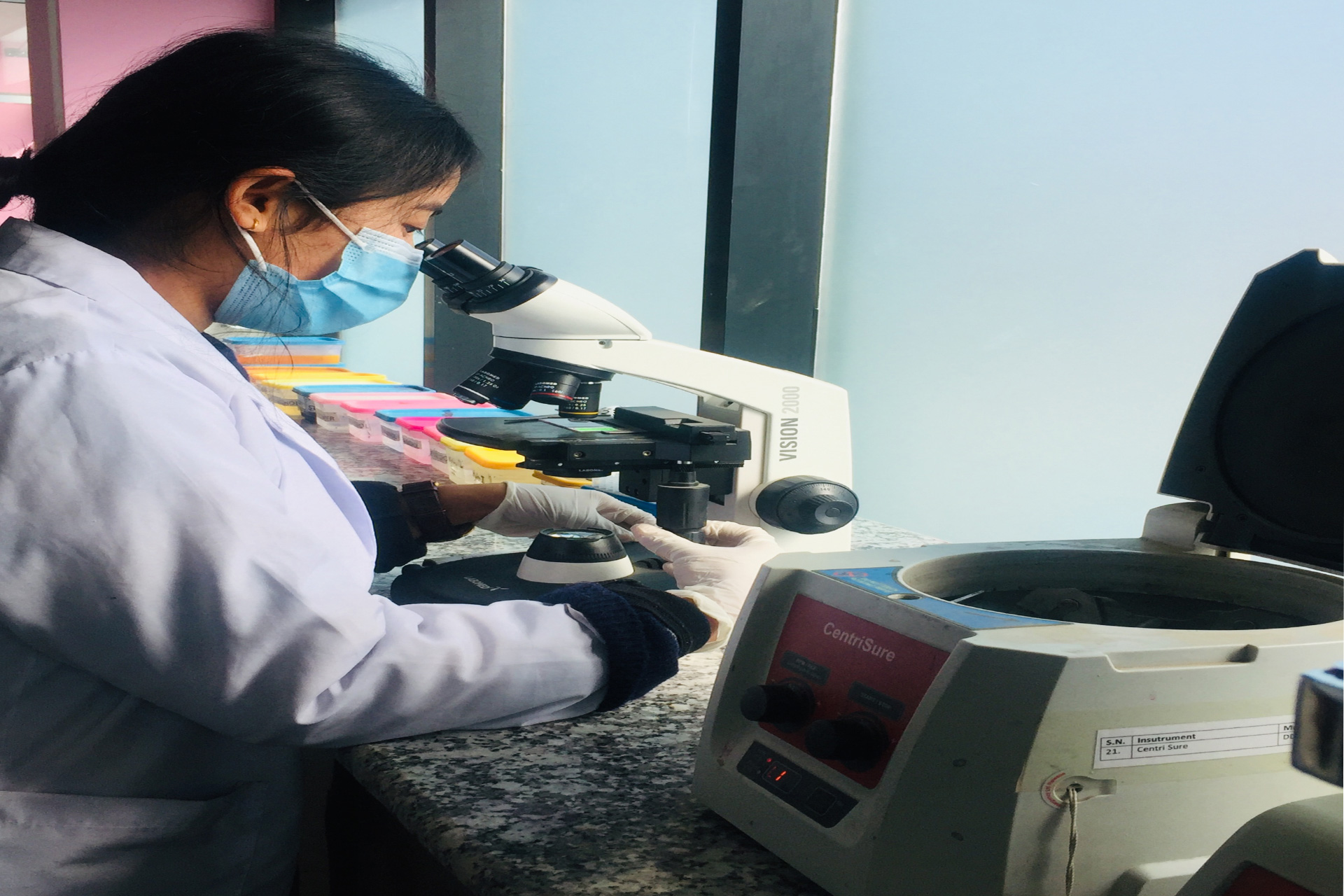
Examination of tissue excised for the diagnosis is Histopathology. It remains the final diagnosis in most of the cases and is gold standard method of diagnosis in various disease conditions. When treating physician, excise entire organ or tissue, it is received by the pathology laboratory. The specimens received by the pathology laboratory are then analysed using various techniques.
Principally, there are two types of specimens:
- Large specimen which include whole or part of an organ removed during treatment. e. g. Gall bladder during cholecystectomy
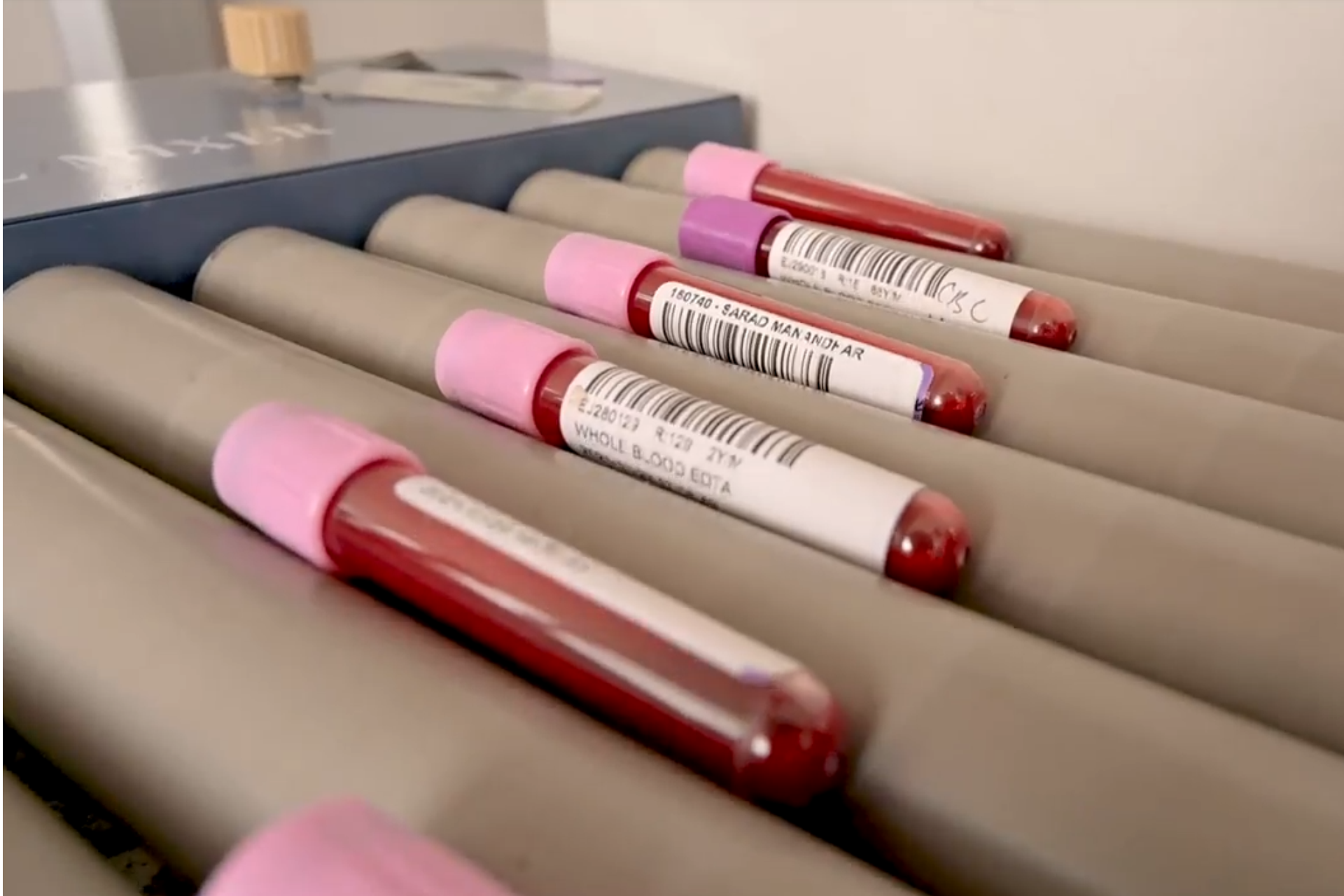
- Smaller bits of tissue which is removed as biopsies, usually for diagnosis purpose. Biopsies include excision biopsies, in which tissue is removed with a scalpel (e.g. a skin excision for a suspicious mole) or a core biopsy, in which a needle is inserted into a suspicious mass to remove a slither or core of tissue that can be examined under the microscope (e.g. to investigate a breast lump).
Specimens received by the pathology laboratory require initial tissue preparation, then are treated and analysed using techniques appropriate to the type of tissue and the investigation required. It is used to diagnose, cancerous and non-tumorous conditions.





Accurate Product Testing by Expert Scientists